Unix File Permissions :
In previous chapter we have discussed different file commands,directory commands. We had also discussed about process commands with examples and grep command with example in previous articles. In this article i will try to explain the most important topic which is related to Unix File Permissions,directories,how to give the permissions using chmod command. File permissions are most important component of unix operating system because it secures the files by giving the specific permissions.There are following types of permissions :
Owner Permissions :
Owner Permissions are Unix File Permissions given to the specific owner to open,read,write or execute the file
Group Permissions :
Group permissions are Unix File Permissions to specific group of users to open,read,write and execute the file.
World Permissions :
These are Unix File Permissions to other user to perform open,read,write, execute file permission.
1) Default Permissions for Regular File:
Open File Read
Write or Modify Write
Execute Read & Execute
Default:
| rw – | r – – | r – – |
User Group Others
2) Default Permissions for Directory File:
ls à Read
Create or Delete Files à Write
cd à Read & Execute
Default:
| rwx | r – x | r – x |
User Group Others
$ ls –l à To check permissions on files
chmod:It is used to change file permissions
Syntax:
chmod who/[+,-,=]/Permission File_Name/Directory_Name
Who: Permissions:
User/Owner u (+) Add Permission Read r
Group g (-) Deny Permission Write w
Other o (=) Assign Permission Execute x
Examples:
1) $ chmodu+xPermission_File
It adds Execute Permission to User Members
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
2) chmod u-wx,g-x,o-x Permission_File
It removes Permissions of Write, Execute for User and Execute for Group & Others from Permission_File
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
3) $ chmod u=w Permission_File
It adds only Write Permission to User members and it deletes Read and Execute Permission from User members.
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
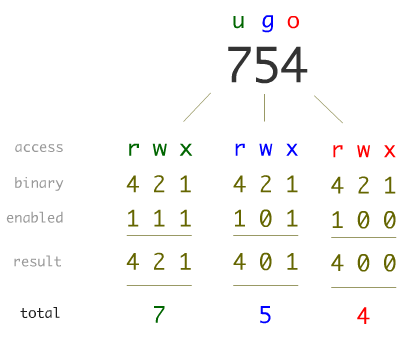
| Octal Code (2nd Method)
Read 4 Write 2 Execute 1 |
| 0 No Permissions 4 r
1 x 5 r, x 2 w 6 r, w 3 w, x 7 r, w, x |
1) chmod 477 Permission_File
It gives Read Permission to User, Read/Write/Execute Permissions to Group & Others.
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
2) chmod700Permission_File
It gives Read/Write/Execute Permission to User and No Permissions to Group & Others
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
3) chmod777Permission_File
It gives Read/Write/Execute Permission to User, Group & Others
$ ls –l Permission_File& see the O/P
4) chown:To change Owner of the File/Directory
Syntax:$ chownOwner_Name File/Directory
5) chgrp: To change Group of the File/Directory
Syntax:$ chgrpGroup_Name File/Directory
UMASK:
Default file creation permissions will be obtained from the umask value. Mask of umask will give the actual permissions. Mask is subtract value from 7
If umask is 021, then the default file permissions are 7-0,7-2,7-1
i.e. 756 are the permissions (rwxr-xrw-)
The current umask value can be had by:
$ umask
0227
first 0 indicate the value is octal; umask can be assigned new value by:
$ umask 042.
Click on Topic You want to learn:
- History of SQL
- SQL Create Table(DDL in SQL)
- SQL DML Statements(INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE)
- SQL Select Statement Execution
- Operators in SQL
- Views in SQL
- Materialized View in SQL
- Joins in SQL
- Inner Join / Outer Join
- Full Outer Join / Cartesian Join
- Union and Union ALL
- Intersect and Minus
- Indexing in SQL
- Rank and Dense Rank
- SubQueries and Correlated Subqueries
- Parser and Optimizer
- Oracle 11 G new Features
- SQL Functions List
- Constraints in SQL
- Database Normalization
- Table Partitioning
- Pivot in SQL
- Difference Between Truncate,Delete and drop
- Oracle System Tables
Unix Tutorials :
4.Create File in Unix using multiple ways
12.paste Command
Hope you like this article.If you like this article dont forget to comment in comment section.